Explain Why Earth's Early Atmosphere Differs From Earth's Atmosphere Today
When that magma nears the surface those gases are released into the surrounding air. There was also no ozone layer to absorb the suns ultraviolet rays.
Study Suggests Early Earth S Atmosphere Was Rich In Carbon Dioxide Earth Earthsky
Instead of the familiar oxygen and nitrogen our early atmosphere would have been a toxic mixture of methane ammonia hydrogen and water vapour.

. It is suggested that from the time of the earliest dated rocks at 37 billion years ago Earth had an oxygenic atmosphere. As carbon dioxide was broken down by cyanobacteria more CO 2 could be dissolved into. It is possible that some of these organic molecules arrived on the early Earth on meteorites and comets from space.
The planet is generally thought of as having three distinct atmospheres over the course of its lifetime. Scientists have found organic compounds including amino acids in modern meteorites that have landed on Earth. Today as during the earliest days of the Earth magma flowing from deep in the Earth contains dissolved gases.
The findings rest on the widely held theory that Earths atmosphere was formed by gases released from volcanic activity on its surface. Around 42 billion years ago Earth cooled enough for the surface to solidify and for water vapor to condense and fall as rain. And yet the Earths early atmosphere somehow transformed into the life.
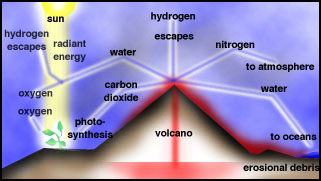
The first atmosphere was formed by outgassing of gases trapped in the interior of the early Earth which still goes on today in volcanoes. As Earth cooled an atmosphere formed mainly from gases spewed from volcanoes. Water vapour condensed to form the oceans.
When the planet first cooled down 44 billion years ago. Scientists believe that the evolution of life changed the atmosphere. And it looked nothing like what we have today.
Early oxygen bonded with iron to form a layer of rust but eventually began to build up in Earths atmosphere. For the Early Earth extreme volcanism occurred during differentiation when massive heating and fluid-like motion in the mantle occurred. Early Earths Atmosphere was Similar to Present-Day One.
There is evidence that the Earths early atmosphere contained less oxygen but more carbon dioxide and water vapour than it does today. The composition of the atmosphere has changed since the Earth was formed 45 billion years ago. Natural processes and human activity have changed the atmosphere and continue to change it today.
Lower altitudes also have quantities of water vapor. Around 44 billion years ago crust solidified and numerous volcanoes formed ejecting steam carbon dioxide and ammonia into the skies. Photosynthesis caused the amount of.
The early atmosphere of the Earth was comprised primarily of hydrogen and helium. The Earth its oceans and atmosphere are made of elements and compounds in different states. The only trend in recent literature is the suggestion of far more oxygen in the early atmosphere than anyone imagined.
It included hydrogen sulfide methane and ten to 200 times as much carbon dioxide as todays atmosphere. The atmosphere we enjoy today is radically different from the atmosphere that formed with the Earth billions of years ago. Over time the density of these volcanic gases became sufficient to form a second Earths atmosphere primarily of carbon dioxide and water.
For the three billion years or so the Earth was scalding hot molten for the most part. Why do scientists think that Earths atmosphere today is different to its early atmosphere. The early Earths atmosphere contained almost no oxygen and was much warmer than it is today.
When earth was first formed its atmosphere was likely composed of hydrogen helium and other gases that contained hydrogen. Astronomical and geological evidence suggests that active volcanoes covered early Earth. See the explanation below.
In addition with no protective atmosphere Earth was probably very hot and constantly bombarded with comets and asteroids. This is unanswerable until you determine what you mean by early Earth. It is believed that there was intense volcanic activity for the first billion years of the Earths existence.
The early atmosphere was probably mostly carbon dioxide with little or no oxygen. The particle model may be used to explain the different properties of. It is likely that the bulk of the atmosphere was derived from degassing early in the Earths history.
The early atmosphere was mainly carbon dioxide and water vapour. Scientists from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have found that the atmosphere of Earth just 500 million years after its creation was. Molecules of hydrogen and helium move really fast especially when warm.
It was completely uninhabitable even before the hypothetical catastrophic impact that completely melted the crust of the planet and put enough material into space to create the. What areas and atmospheres do scientists study where there is no life. The Earth and its atmosphere were very hot.
The atmosphere we have today is very different from the Earths early atmosphere. Earths original atmosphere was probably just hydrogen and helium because these were the main gases in the dusty gassy disk around the Sun from which the planets formed. Yet this atmosphere didnt last for very long because the solar wind from the sun blew it away.
The surface was molten. When Earth formed 46 billion years ago from a hot mix of gases and solids it had almost no atmosphere. The synthesis of small organic molecules from the mixture of gases in the atmosphere may not have been necessary.

Hydrosphere Origin And Evolution Of The Hydrosphere Britannica
No comments for "Explain Why Earth's Early Atmosphere Differs From Earth's Atmosphere Today"
Post a Comment